About the Low-Toxicity Gold Dissolution Mechanism of GDA
This paper illustrates while GDA has low toxicity while possessing a high gold dissolution ability as well as that of sodium cyanide.
1.A Brief Introduction of the Human Respiratory System
Normally, the human body inhales the O2 and exhales the CO2. The histocytes use the O2 to oxidize sugar, fat, protein (which were called as a substrate in biochemical) within the human body and produces H2O, ATP energy and CO2. The completion of the biological oxidation process requires the "cytochrome oxidase" to work as a catalyst. Cytochrome a3 can be directly oxidized by oxygen molecule throughout the respiratory chain. Firstly, due to the catalysis of dehydrogenase, 2 Fe3+ in the a3 obtain 2 electrons from the substrate and are reduced to 2 Fe2+. Then, oxidized into 2 Fe3+ again, the 2 Fe2+ lost 2 electrons, which recipient is oxygen. Thus, the oxygen was activated to O2-. Due to the catalysis of dehydrogenase (E), two H+, released by the substrate, combine with O2- to produce water and unleash energy ATP. With gains and losses of electrons, cytochrome oxidase catalyzes the cyclic reaction of Fe2+ and Fe3+ and ensures that O2 is constantly utilized by histocytes.
2.The Biochemical Mechanism of Cyanide Poisoning
When HCN enters the body, a pair of lone electrons on the carbon atom of CN-, a strong coordination complexing agent, can easily coordinate to the metal ion of the cytochrome a3 orbital. Affinitive to each other, CN- combines with Fe3+ in a3 (Fe3+) and form E (Fe3+) CN, that is cyanide cytochrome oxidase (poisoned enzyme). Because of the structural change of the enzyme, the catalysis of cytochrome oxidase disappears and the electrons can no longer be obtained from the substrate, as a result of which E (Fe3+) cannot be reduced to E (Fe2+). Due to the interruption of this step, the whole biological oxidation process is destroyed, and the molecular O2 in the blood can no longer be used by histocytes. Lack of energy, cells are suffocated due to blocked oxidative phosphorylation and reduced ATP synthesis. Therefore, cyanide poisoning is not caused by the lack of O2 in the human body, but the dysfunction of O2 utilization. Biologically, it is known as intracellular asphyxia. Sodium cyanide is a highly toxic chemical product. The aerosol of sodium cyanide of 40~90 mg/m3, if inhaled by animal for 25 to 43 minutes, will cause the symptom of irritation on mucosa, shortness of breath, excitement and salivation; The lethal inhalation dose of the aerosol is 150~170 mg/m3 for 62-76 minutes, or 400~500 mg/m3 for 10-20 minutes. The oral LD is about 1~2 mg/kg for human beings. Common causes of death caused by sodium cyanide are inhalation of sodium cyanide dust during production at room temperature, and vapor inhalation during heat treatment as well as intake by mistake. As one of the most dangerous chemicals strictly controlled by UN, sodium cyanide poses a threat to human being’s production environment.
The chemical formula of sodium cyanide: NaCN
Molecular structure: Na+ [C≡N]-
The chemical equation of sodium cyanide in hydrometallurgy of gold or silver is as follows:
4Au+8NaCN+2H2O+O2=4Na[Au(CN)2]+4NaOH
3.The Principle of Low Toxicity and Gold Mineralization of GDA:
The main active ingredient of GDA: carbide sodium cyanurate
Chemical molecular formula of carbide sodium cyanurate: C6Na3O3N6
The molecular structure is:
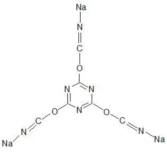
It can be seen from the structure that the cyanide-like form in the CN- branched chain is connected by a covalent bond, rather than an ionic bond, as is the case with sodium cyanide. Because of the structure and steric hindrance, this kind of cyanide usually does not decompose free cyanide (CN-) in an alkaline environment, but it has the complexation similar to that of free cyanide. Working with other ingredients of the product, free cyanide could complex with gold.
In the process of the synthesis of GDA, there is a small amount of cyanide in the product due to some side effects. Although a small amount of cyanide (CN-) is detected, this is the main reason why GDA is of non-toxic or low-toxic for people and other creatures.
The reaction equation of carbide sodium cyanurate dissolving gold is: C6Na3O3N6+Au+H2O+O2→ Au(C6Na3O3N6)2+NaOH
GDA contains a small amount of water-insoluble substance (≤3%), which are mainly iron-containing oxides, and such oxides could further stabilize the carbide sodium cyanurate under the general situation. Therefore, after complete dissolution, there will be some black slag layer at the bottom of GDA solution, which is normal and would improve the safety performance of products without affecting the product's ability to dissolve gold.
